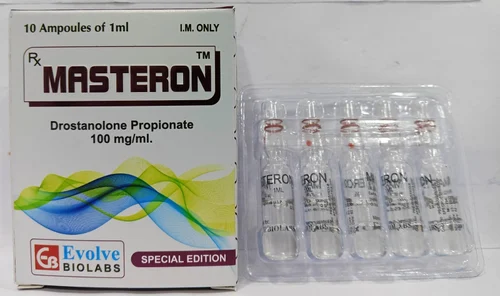
Masteron Propionate
$45.00
Buy Masteron Propionate Online
Buy Masteron Propionate is a well-known compound in the family of anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS). It is derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a naturally occurring hormone in the body. The “propionate” ester attached to its structure is responsible for its faster release and shorter active life compared to longer-ester forms. Because of this, Masteron Propionate is recognized for its rapid onset and quick clearance. It has been studied historically for its medical relevance, particularly in conditions where anti-estrogenic properties are beneficial.
Chemical Nature and Background
Chemically known as Drostanolone Propionate, Masteron belongs to the DHT-derived class of compounds. DHT-based substances typically do not convert to estrogen through aromatization. This characteristic has attracted scientific interest for its potential anti-estrogenic qualities. The propionate ester ensures that the hormone is released relatively quickly after administration, which influences dosing frequency in clinical research environments.
Masteron first gained attention for its potential role in breast cancer treatment, particularly before modern advancements in targeted therapy became available. Its ability to counter certain estrogen-related pathways made it a subject of medical study at the time.
Properties and Characteristics
Masteron Propionate is often discussed for its specific characteristics within research and educational contexts:
1. DHT-Based Structure
Being a DHT derivative, Masteron Propionate does not convert into estrogen. This lack of aromatization is among its defining traits, influencing how it interacts with other hormones in the body.
2. Short Ester, Fast Action
The propionate ester allows the compound to act more quickly. This means it reaches peak levels sooner compared to longer esters. The trade-off is that levels also drop at a faster rate.
3. Potential Hardening Effect (Research Perspective)
In literature focused on physiology and body composition, Masteron is often note for its “drying” or “hardening” influence due to its androgenic profile. These references are observational and not a recommendation for use.
Scientific and Clinical Interest
Historically, Masteron Propionate was studied for:
- Anti-estrogenic potential: Its DHT structure made it a candidate for research relating to estrogen-influenced conditions.
- Body composition effects: Some research observed changes in muscle firmness and water retention.
- Hormone interaction studies: As a non-aromatizing compound, it was analyze in environments where estrogen levels and androgen receptor behavior are key variables.
Modern medicine rarely uses Masteron today due to the availability of more effective, safer, and targeted therapies.
Potential Effects
Masteron Propionate is associated with several physiological effects in research discussions:
Positive Observations
- Lean or “dry” appearance in muscle tissue
- Increased muscle density
- Reduction in water retention
- Strong androgen receptor binding
Possible Negative Effects
Because it is an androgenic compound, Masteron may cause:
- Oily skin or acne
- Possible hair thinning
- Mood fluctuations
- Androgen-related side effects depending on individual sensitivity
These effects are discuss academically and do not imply suitability or recommendation for use.
Safety and Considerations
Masteron Propionate, like all anabolic-androgenic steroids, carries risks and should not be use without proper medical supervision. The compound can influence hormone balance, lipid levels, and overall endocrine function. Non-prescribed or unsupervised use is unsafe and can lead to long-term health consequences.
Conclusion
Masteron Propionate is a DHT-based anabolic compound historically studied for its anti-estrogenic properties and its effects on body composition. While it holds a notable place in the history of performance and hormone research, modern medical practice has largely moved toward safer, more advanced therapies. Today, Masteron Propionate remains primarily a subject of scientific, academic, and historical interest rather than routine medical use.
Be the first to review “Masteron Propionate” Cancel reply
Related products
Injectables
Injectables
Injectables


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.